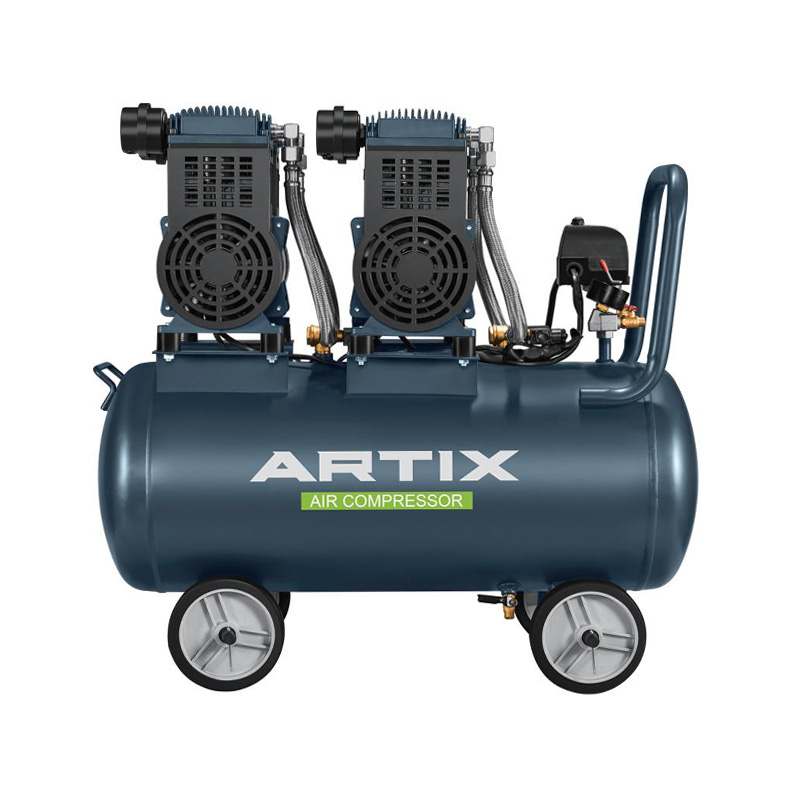
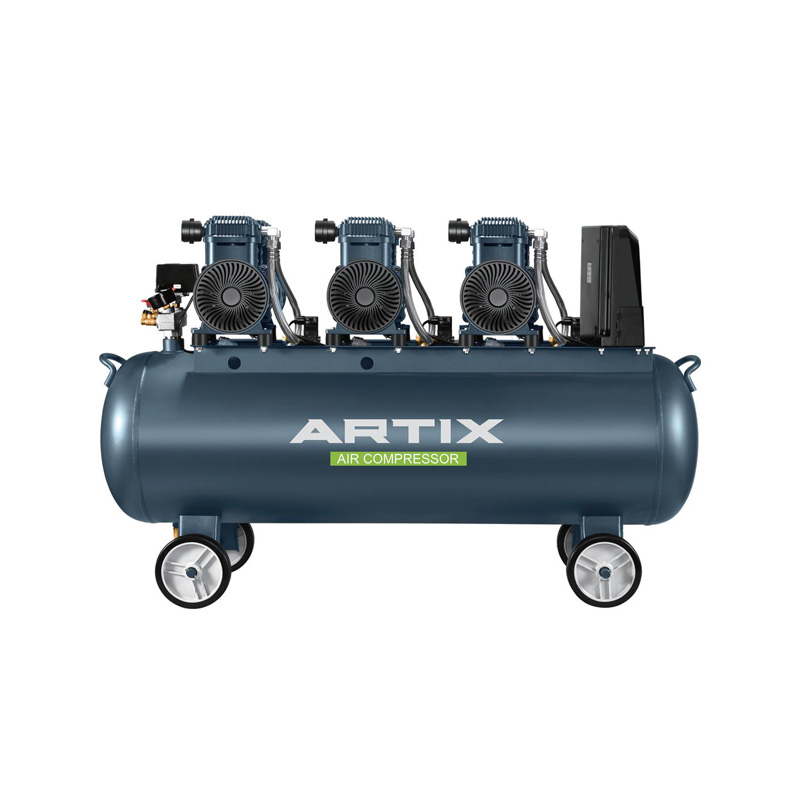
In the industrial world, choosing the right Industrial Air Compressor is essential for maximizing efficiency and minimizing operational costs. Among the various types of compressors available, Direct Driven Air Compressor stands out for their energy-saving benefits, reduced maintenance requirements, and overall efficiency. These compressors play a pivotal role in industries that rely on continuous, high-demand air supply, making them an attractive choice for manufacturers, workshops, and production facilities.
What is a Direct Driven Air Compressor?
A direct-driven air compressor is a type of compressor where the motor is directly connected to the compressor's crankshaft. Unlike belt-driven models, which use belts to transfer power from the motor to the compressor, direct-driven compressors eliminate the need for belts and pulleys. This setup results in a more streamlined and compact system with fewer moving parts.
Here’s how a typical Industrial Air Compressor works:
Motor-driven compression: The electric motor powers the compressor directly.
Air intake: Air is drawn into the compressor chamber.
Compression: The motor-driven piston or screw mechanism compresses the air.
Discharge: The compressed air is then released for use in various industrial applications.
Because the motor is directly coupled to the compressor, there is less energy loss in the system compared to belt-driven compressors. This means more power is efficiently transferred to the air compression process, improving the overall performance of the compressor.
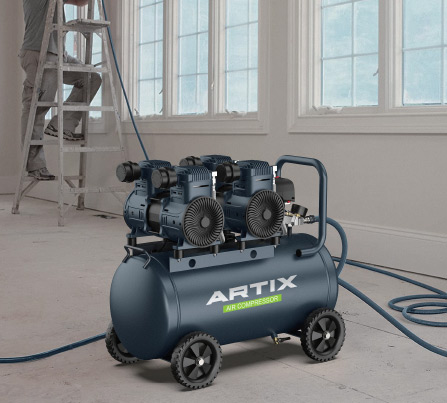

Why Direct Driven Air Compressors Are More Efficient
Direct-driven compressors are widely recognized for their efficiency, particularly in industries that demand continuous air supply. Below are some of the key reasons why these compressors are considered more efficient than traditional models:
1. Reduced Energy Loss
One of the main advantages of Direct Driven Air Compressors is their ability to transfer power more effectively. With fewer components such as belts or pulleys, the energy loss associated with the mechanical transfer is significantly minimized. In contrast, belt-driven compressors have friction and energy loss at the point where the belt meets the pulley.
2. Fewer Moving Parts
Since direct-driven compressors have fewer moving parts than their belt-driven counterparts, there are fewer components that could wear out or require maintenance. This means less downtime, fewer repairs, and a longer lifespan for the compressor.
3. Better Performance at High Demand
Direct Driven Air Compressors are particularly effective in environments with high air demand. In industries such as manufacturing, automotive, and heavy-duty machinery, a steady and reliable air supply is crucial. Direct-driven systems excel in these scenarios because they provide consistent performance without the slip or lag that can occur with belt-driven compressors.
4. Improved Reliability and Durability
Without the need for belts, which can stretch or wear out over time, direct-driven compressors have enhanced reliability and durability. The simplicity of the system reduces the chances of breakdowns and keeps maintenance costs low. These compressors are well-suited for continuous operation in industrial settings where performance is critical.
Applications of Direct Driven Air Compressors
Industrial Air Compressors are versatile tools that are used across various industries. Some of the key sectors that benefit from direct-driven models include:
Manufacturing: For powering machinery, tools, and automated systems.
Automotive: To run pneumatic tools, paint sprayers, and air-powered lifting equipment.
Construction: Where reliable, continuous airflow is needed for construction tools and equipment.
Food Processing: To power equipment like conveyor belts, packaging machinery, and air blowers.